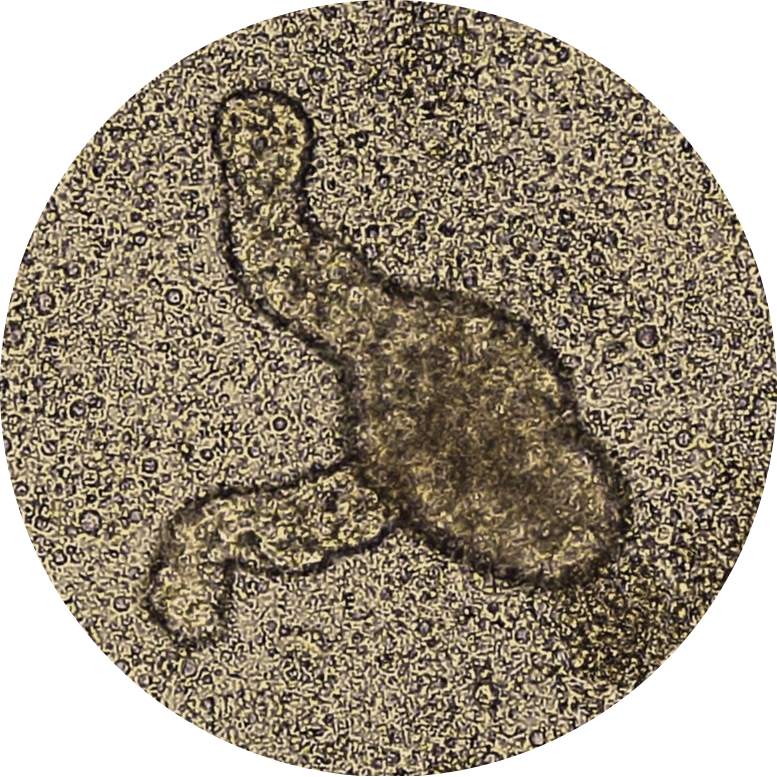
Human iPSC-derived Intestinal Epithelial Cells
These organoids mimic the structure and cellular diversity of human intestinal epithelium.IPSC-derived intestinal products show a crypt-like structure, which is the common feature of intestinal epithelium. They contain enterocytes, goblet cells, Paneth cells, and enteroendocrine cells. They are valuable tools for studying gut barrier function, host-microbiome interactions, screening drugs, assessing pharmacokinetic profiles of potential medications, and testing the toxicology of possible interventions.
Benefits
- Physiological 3D intestinal architecture
- Contains absorptive and secretory cells
- Suitable New Approach Method (NAM) for gut disease modeling
- Develops a high-throughput platform for drug screening and assessing the toxicology of potential drugs.
Product Specifications
|
Feature |
Detail |
|---|---|
|
Identity Markers |
Sucrase isomaltase (enterocytes), (MUC2 (goblet cells), LGR5 (stem cells), Lyz (Paneth cells) |
|
Quantities |
≥ 500 organoids/ crypt like structures per vial |
|
Quality Control |
Markers characterization , mycoplasma testing |
|
Format |
Cryopreserved |
|
Donor & Reprogramming |
Healthy/ diseased donor-derived iPSCs; Sendai virus reprogramming |
|
Supplied with |
Handling guide and instructions for differentiation and culture |
Explore Epithelial Cells
Advance your tissue modeling and regenerative medicine research with high-quality, iPSC-derived epithelial cells engineered for consistency and performance. Explore the product details to discover how these cells can support barrier function assays, toxicity screening, and disease modeling studies.